
Health Screening Results Review
Review of your health screening results completes your health screening with us.
We encourage a complimentary teleconsult with our doctors for added convenience, during which we will review your results and recommend lifestyle changes. Where necessary, we may arrange to see you at our clinics.
Face to face review at Paragon or any of Minmed Clinics is available @ $10.90 inclusive of GST. Please email us at [email protected] to schedule an appointment.
Post Screening Advisory
- No definite diagnosis may be made from health screening test results alone, and test results should be correlated with your medical history and other clinical findings.
- Screening tests may carry limitations in the capacity to identify or rule out the presence or absence of a condition. Normal health screening test results may not necessarily mean the absence of a medical condition.
- The majority (about 95%) of a normal population test results will fall within the normal range. About 5% of the normal population test results may be slightly above or below the normal level.
- It is an acceptable fact that a normal person’s health screening test results may fluctuate at different times although still within the normal range. This occurrence may be due to diet or other factors.
Book Teleconsult Review
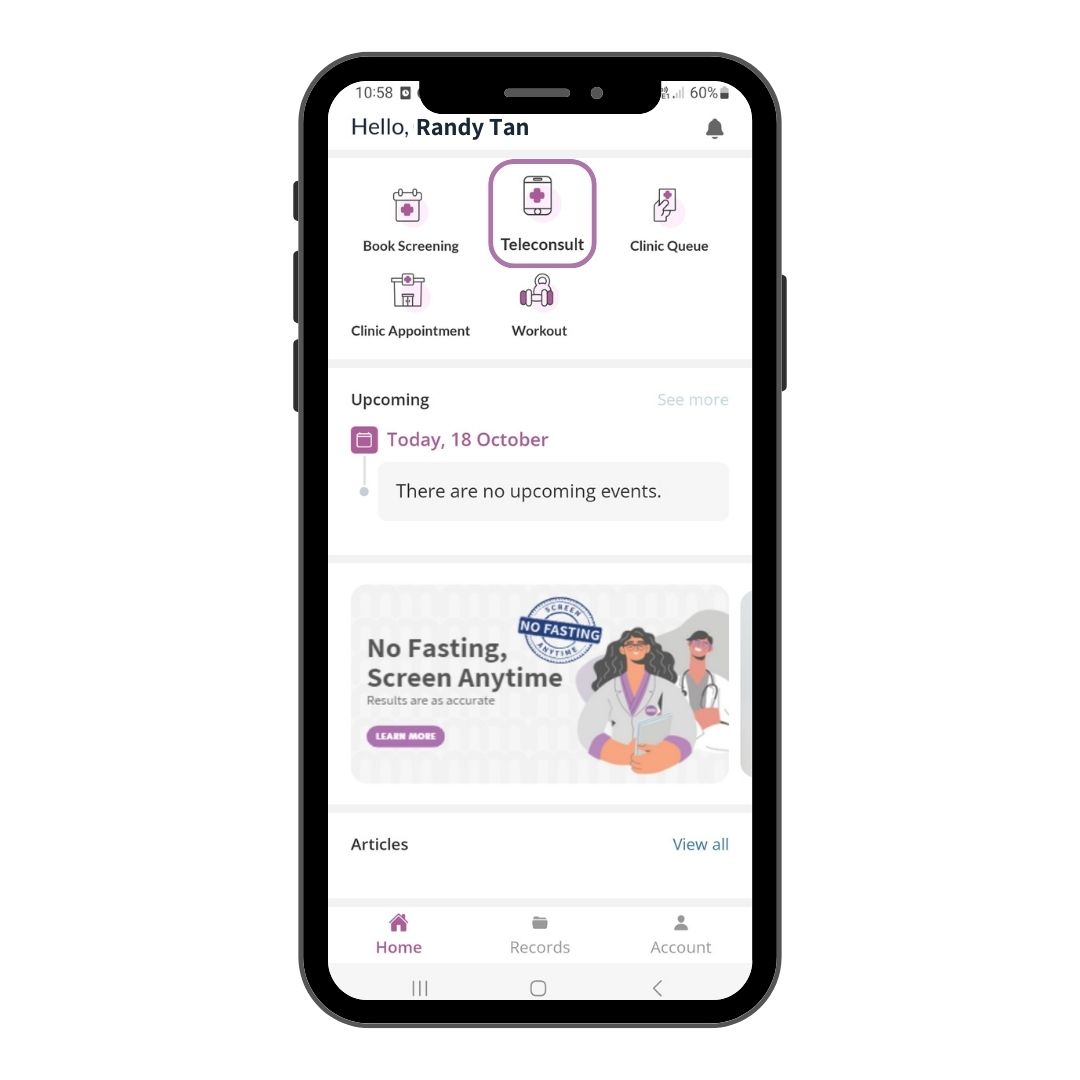
Step 1
Download our app, create an account and select Teleconsult
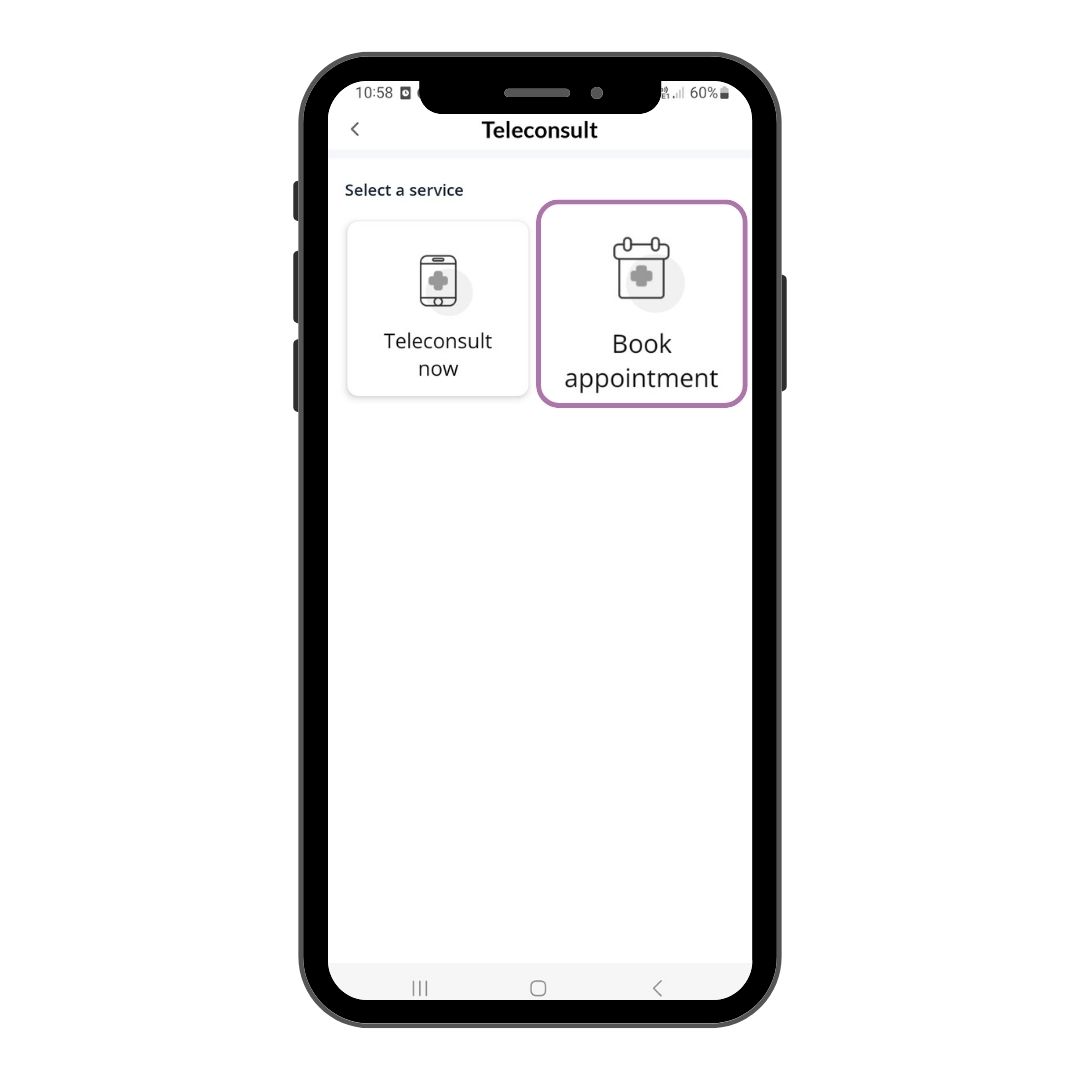
Step 2
Select Book Appointment
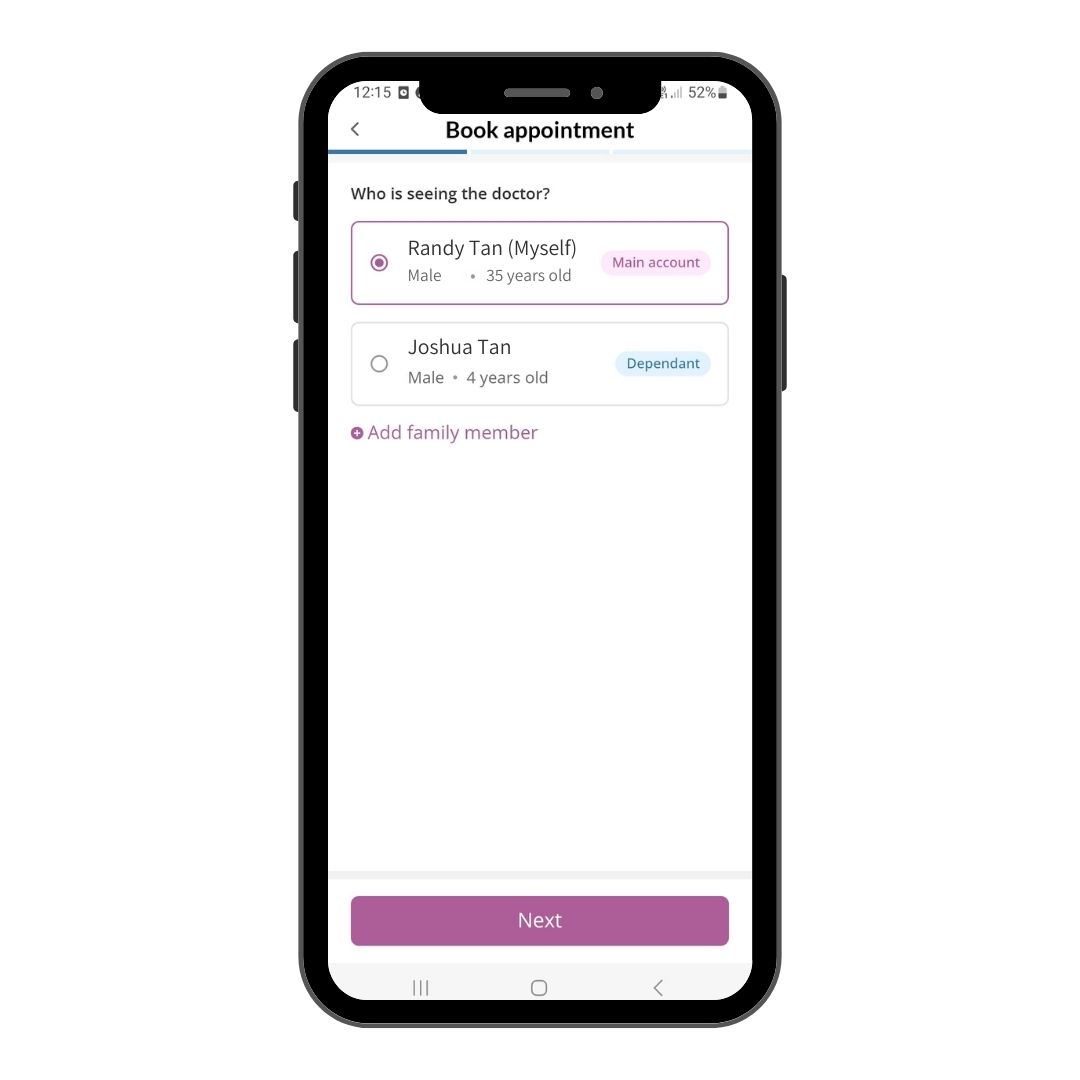
Step 3
Select the correct profile for the review
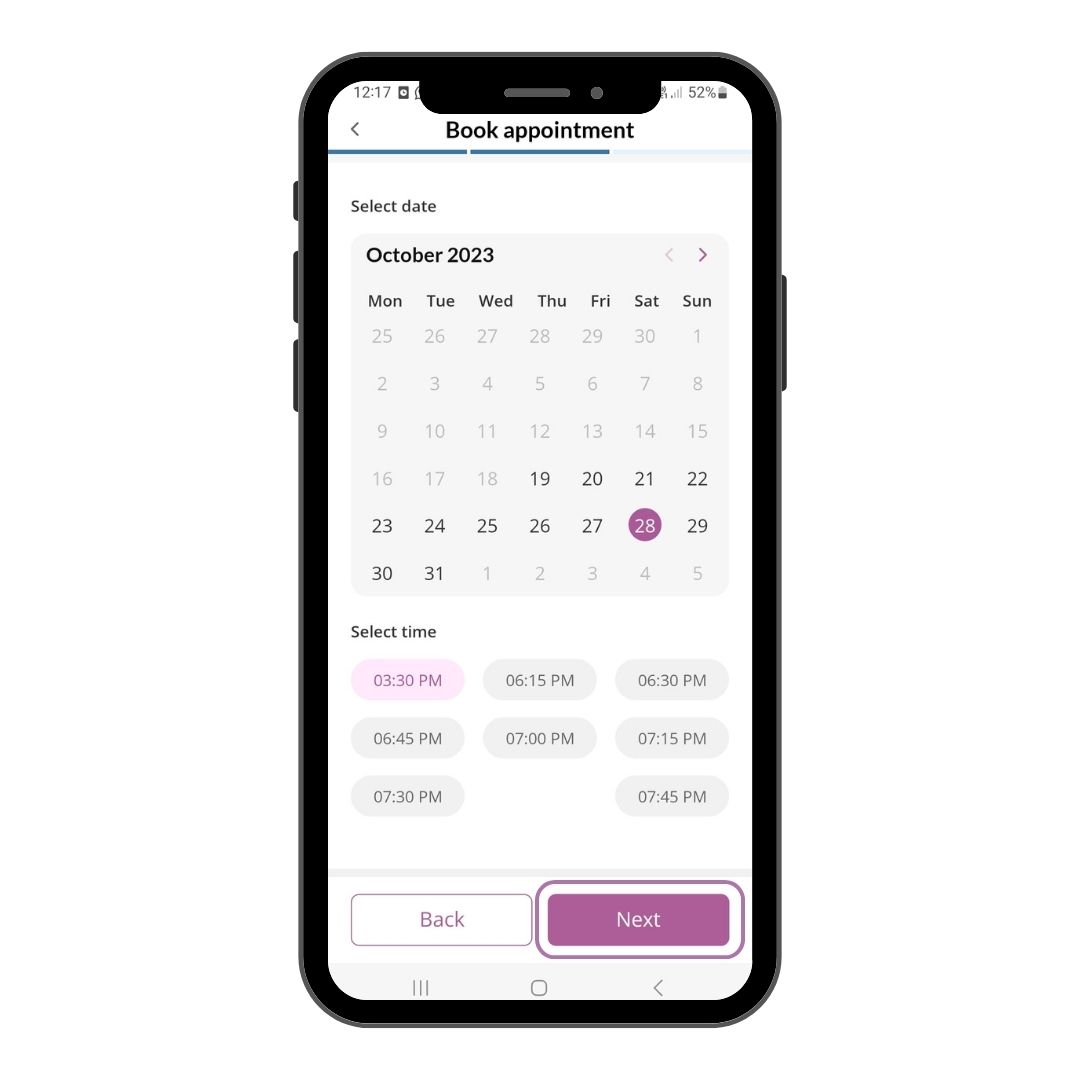
Step 4
Select your preferred date and time for the review
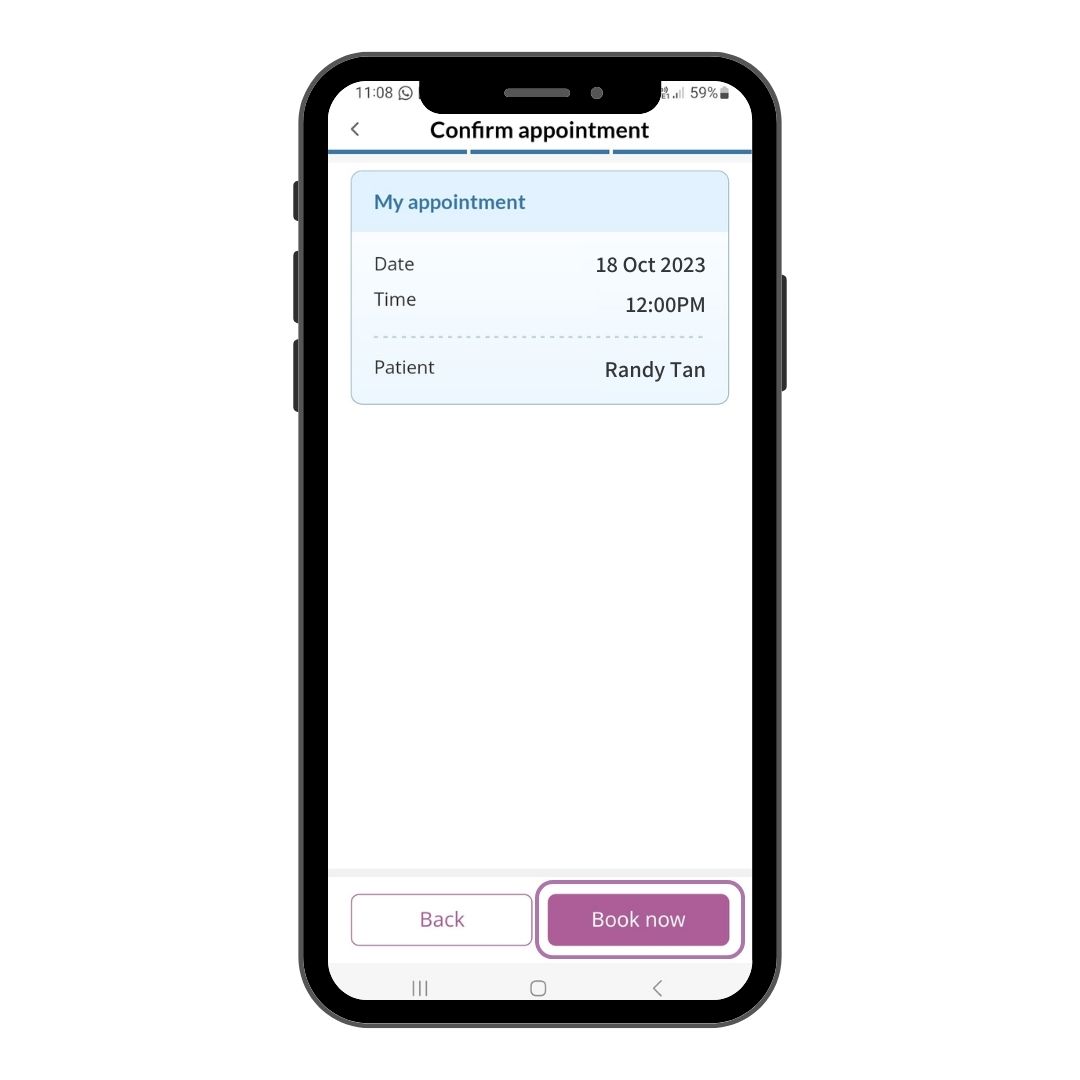
Step 5
Click Book Now
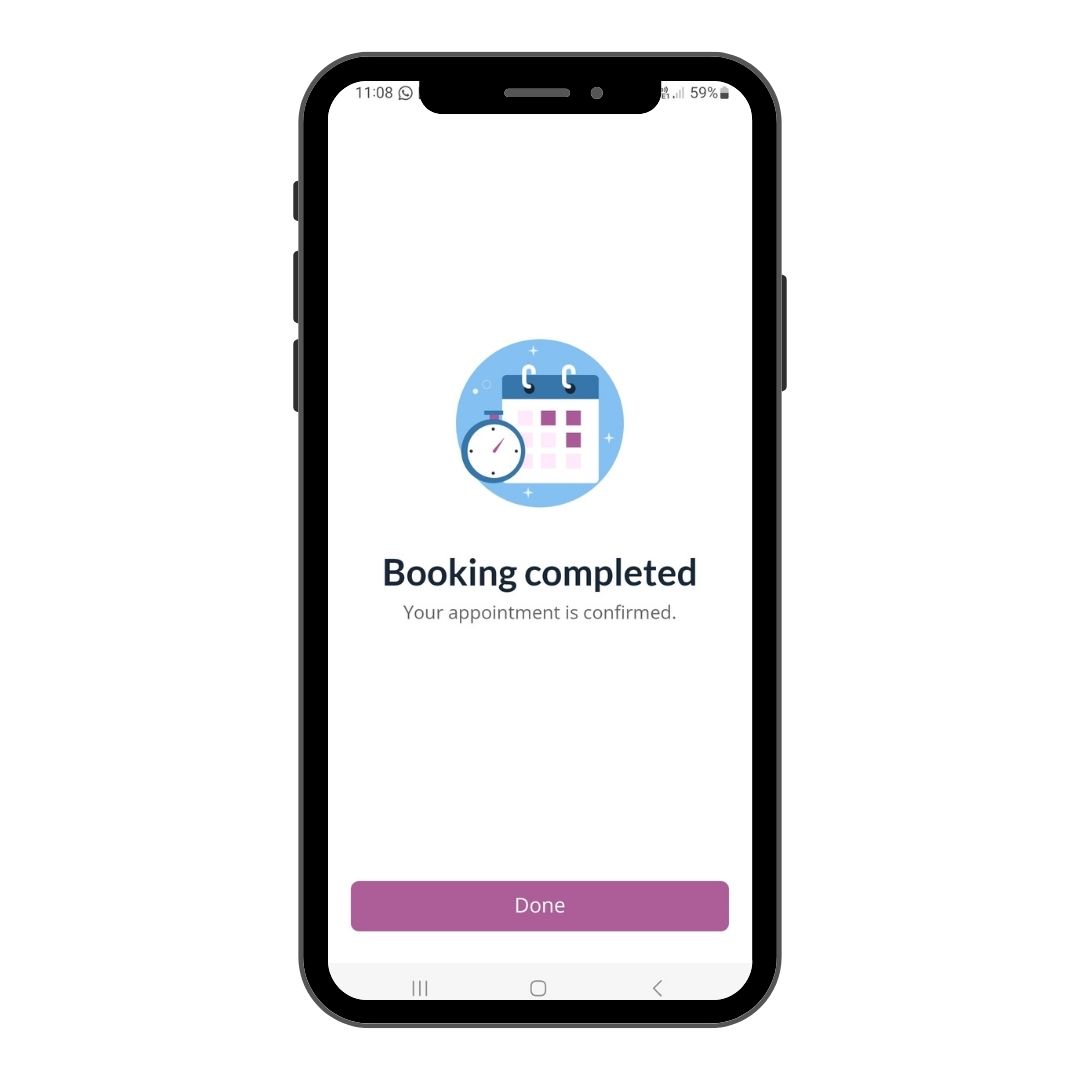
Step 6
Your Teleconsult Review has been successfully booked
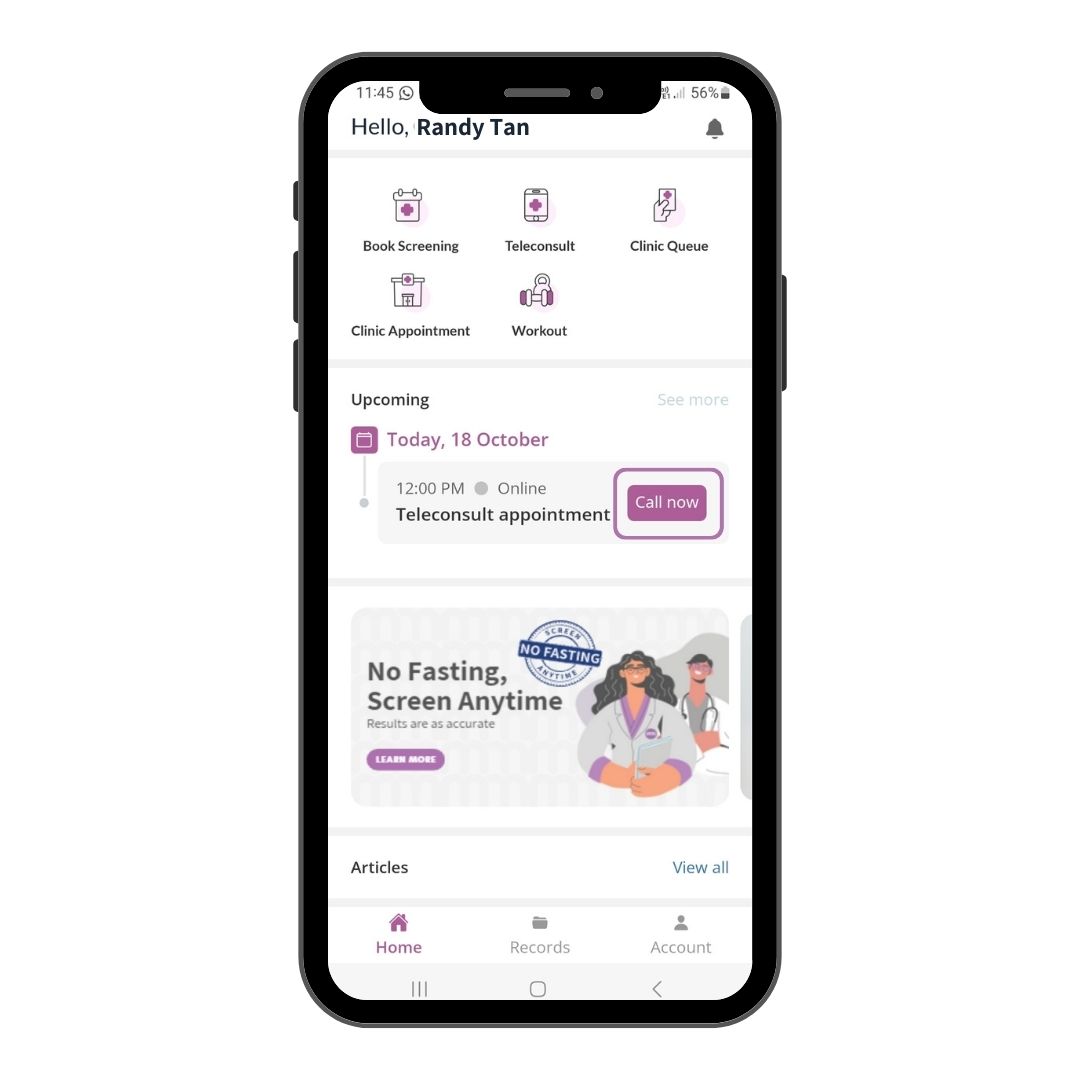
Step 7
Click on Call Now to begin your review
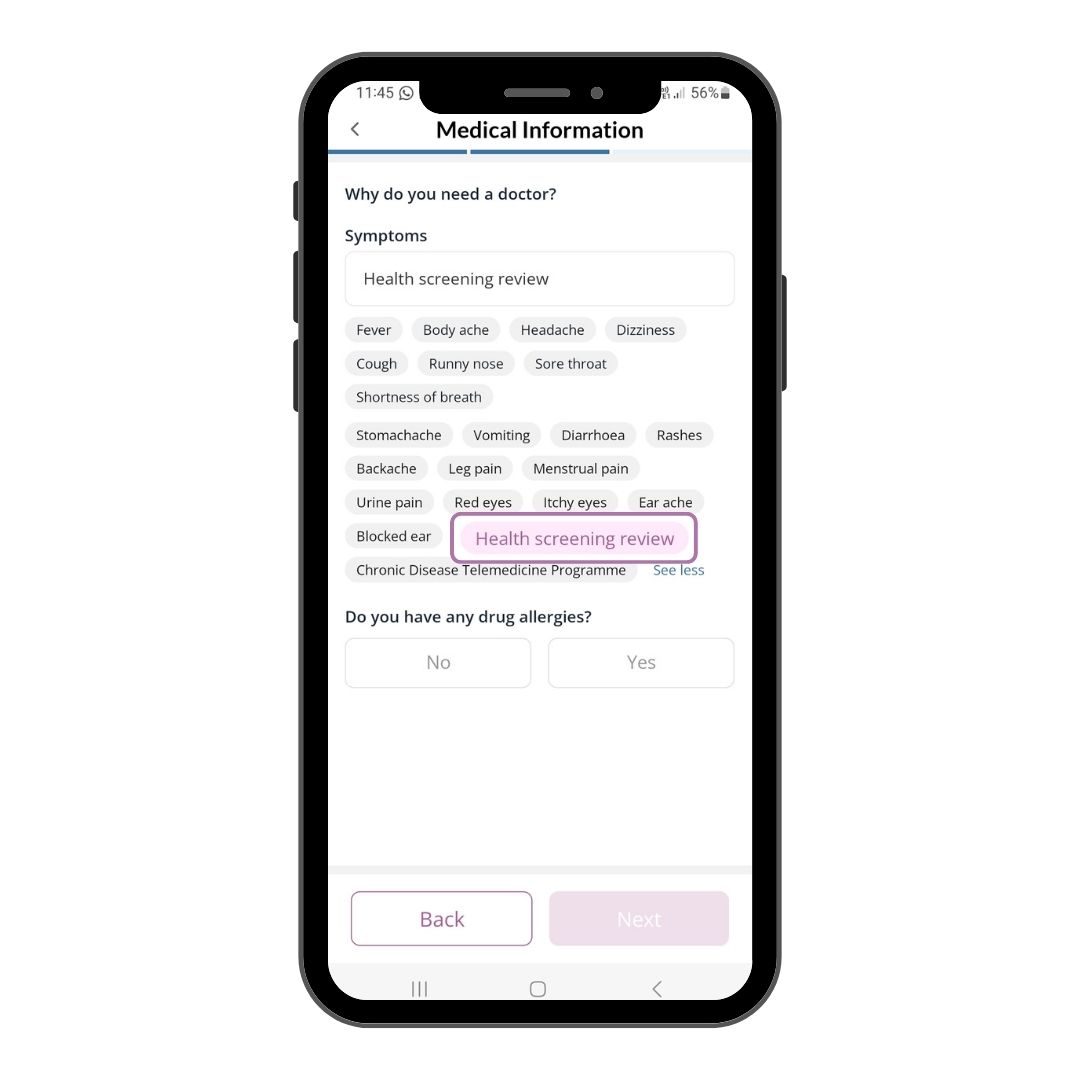
Step 8
Select Health Screening Review, indicate accordingly for any drug
allergy, if applicable
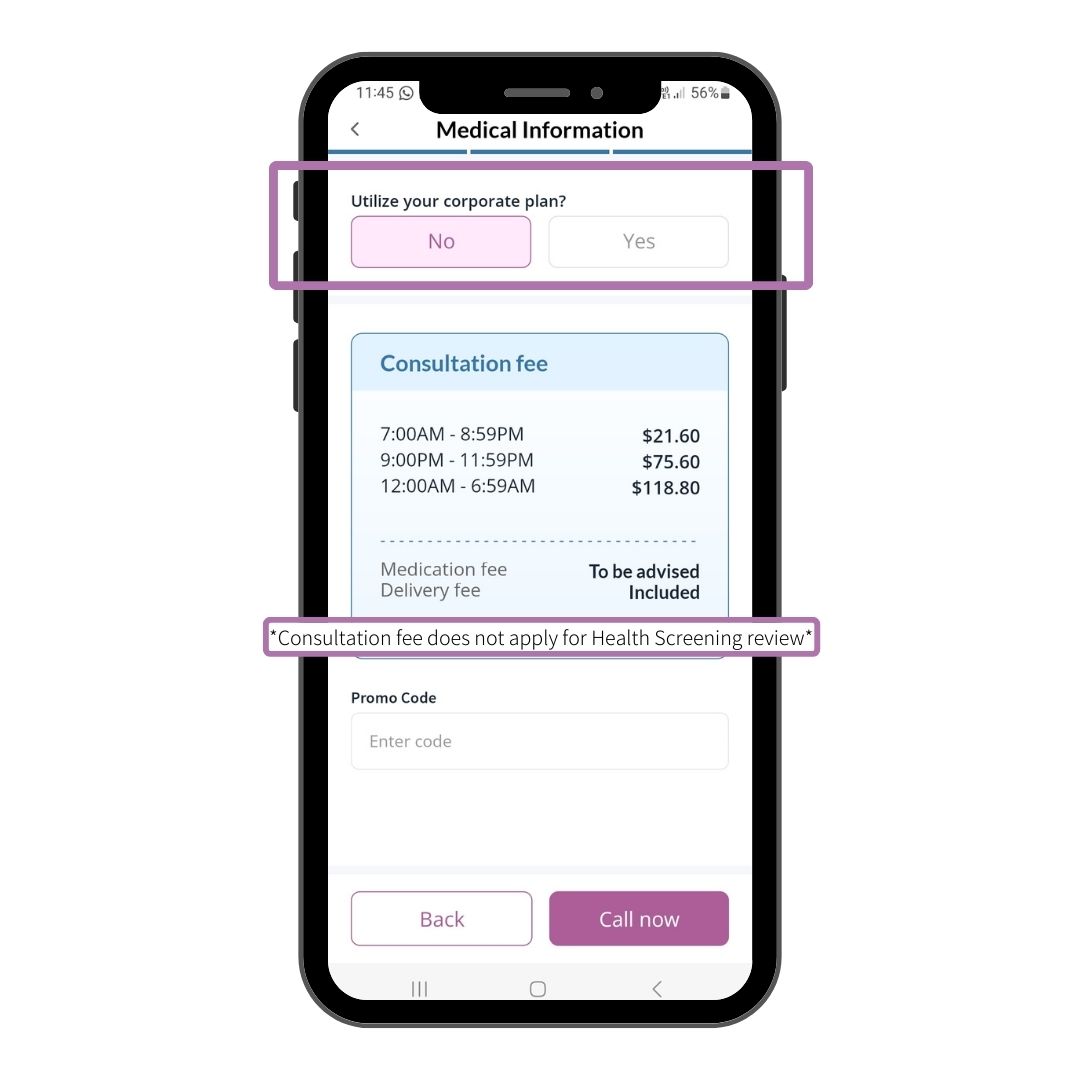
Step 9
Select No under Corporate Plan and click Call Now
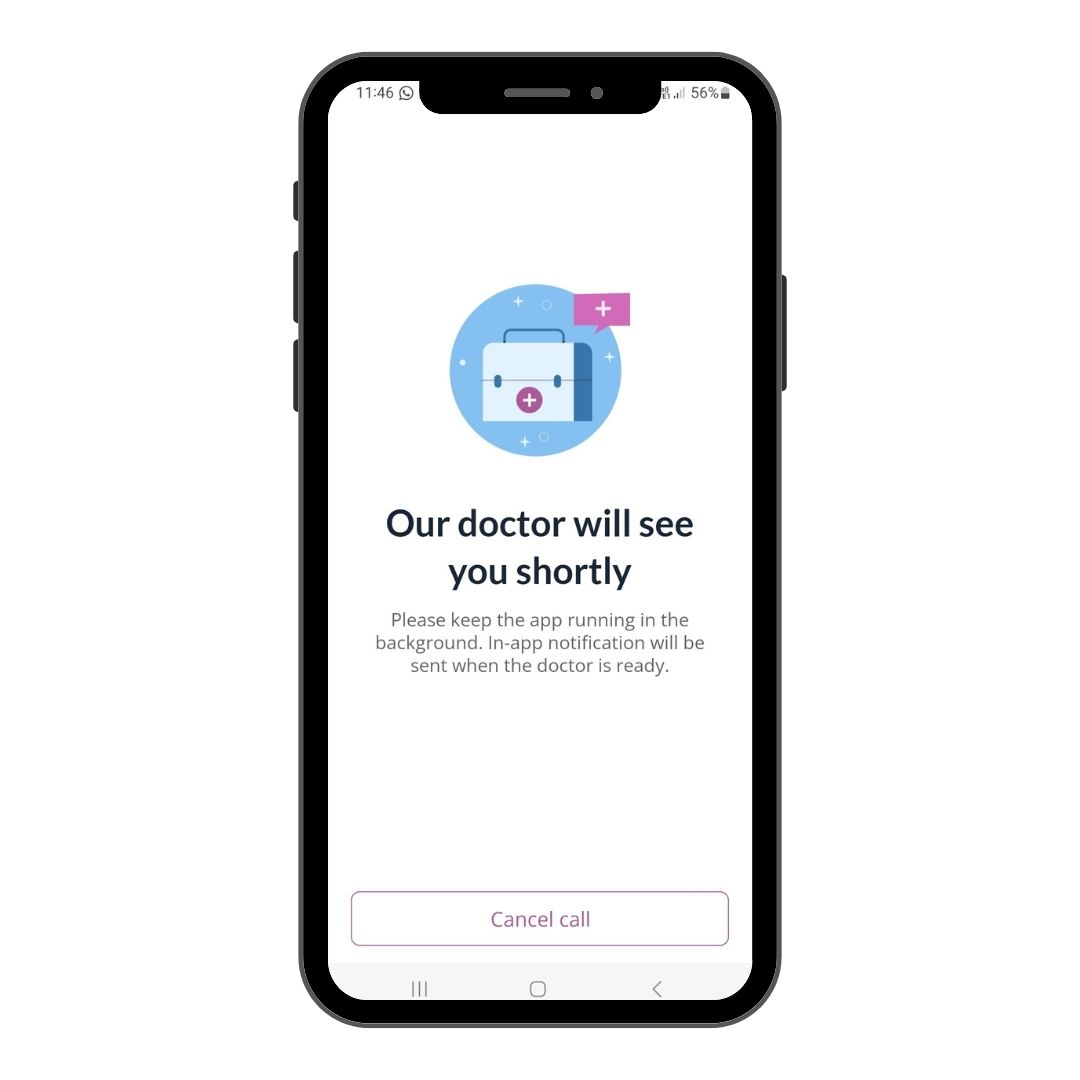
Step 10
Success! Your session will begin shortly.
Screening Glossary
Glossary
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is calculated by BMI = Weight (in kg) / [Height x Height] (in metres).
| BMI in kg/m² | Weight Category* |
|---|---|
| More than or equal to 30 | Obese |
| 25-29.9 | Overweight |
| 18.5-24.9 | Healthy weight |
| Less than 18.5 | Underweight |
*According to the World Health Organization for adults aged 18-69.BMI less than 18.5 presents a risk of osteoporosis in the long term.Obesity (BMI > 30) is associated with increased cardiac risk. 24.4% of our adult population is overweight & 6% are obese. Gradual weight loss of no more than 1kg/week is encouraged using a combination of exercise as well as caloric control.
The blood pressure (BP) typically has 2 readings, a systolic reading which marks the peak blood pressure within the artery when the heart contracts, and a diastolic reading which marks the trough blood pressure within the artery when the heart relaxes before the next beat. Both readings are important in categorisation, and category limits apply to all irrespective of age and gender.
| Category | Systolic BP (mmHg) | Diastolic BP (mmHg) (Heart muscle relax) |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | Below 130 | Below 80 |
| High Normal | Between 130 to 139 | Between 80 to 89 |
| Hypertension (High Blood Pressure) |
140 and above | 90 & Above |
If your blood pressure is in the High Normal category, it is important to focus on lifestyle change.
- Reduction of salt intake
- Regular exercise
- Management of stress
If blood pressure readings are in the hypertensive range, a 2nd reading taken at least 1 week apart is necessary to establish hypertension. Medication may be instituted if the readings remain high despite lifestyle measures described above.
In some instances, blood pressure readings may be on the low side i.e. systolic < 100 and/or diastolic < 60. Whilst this is not a diseased state, persistently low blood pressures may result in occasional giddiness. The use of a home BP monitoring set is highly useful for monitoring blood pressure. We encourage a record of BP readings using either readily available health apps or manual records. Your doctor can then reliably depend on the blood pressure trend to guide your treatment.
Hip and waist measurements help to assess the relative distribution of fat in the abdominal region vs that of the hips and thigh. The Waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) is a useful determinant of risk.
WHR = Waist measurement / Hip measurement
| Body Shape | Health Risk |
|---|---|
| Apple – WHR above 0.8 for women, above 0.9 for men
If you have an “apple-shaped” body habitus, your waist size is larger than your hip size. |
Most of the fat in an apple-shaped person is distributed around the internal organs in the abdomen area. This can be associated with a greater risk of heart disease, diabetes and stroke. |
| Pear – WHR below 0.8 for women, below 0.9 for men
If you are a pear type, your hip section is likely to be wider than your upper body, with most of the fat deposited around your thighs, hips and buttocks region. |
Having a pear body shape indicates a lower metabolic risk compared to an apple body shape. |
Body fat percentage is estimated using the bioelectrical impedence method. It is the proportion of the weight of body fat to the total body weight.
| Gender | Fat percentage |
|---|---|
| Males satisfactory range | 10-20% |
| Females satisfactory range | 20-30% |
Increased visceral fat contributes to an increased risk of high cholesterol, diabetes, hypertension, heart disease and stroke. Reduction of dietary fat and oily/sugary foods, as well as a reduction in total caloric intake will help to reduce body fat.
Visual acuity is a measurement of a person’s ability to see distant objects well. This is assessed by way of individually testing each eye’s ability to read a series of numbers or letters on the “Snellen’s chart”.
A person with poor visual acuity could have underlying issues with short-sightedness (myopia), astigmatism, cataract, or other eye diseases, and follow up with an assessment by a qualified optician and/or ophthalmologist is recommended.
Colour perception is the ability of the eye to differentiate colours. A simple test with the Ishihara’s test will detect red-green colour deficiencies commonly known as colour-blindness.
Colour blindness is typically an inherited genetic disorder, with males more commonly affected than females. Occasionally, acquired causes like disease, drugs and chemicals may cause it.
There is no known cure, but diagnosis can alert the person to make certain adaptations and avoid certain occupations which require precise colour differentiation.
The lipid blood profile which has to be taken in the fasting state comprises the following:
- Total cholesterol
- HDL cholesterol (“Good” Cholesterol)
- LDL cholesterol (“Bad” Cholesterol)
- Total Cholesterol/HDL ratio
- Triglyceride
| Total Cholesterol | Mmol/L | Mg/dL |
|---|---|---|
| Desirable | Below 5.2 | Below 200 |
| Borderline High | Between 5.2 to 6.1 | Between 200 to 239 |
| High | 6.2 & Above | 240 & Above |
| HDL | Mmol/L | Mg/dL |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Below 1.0 | Below 40 |
| Desirable | Between 1.0 to 1.5 | Between 40 to 59 |
| High | 1.6 & above | 60 & above |
| LDL | Mmol/L | Mg/dL |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal | Below 2.6 | Below 100 |
| Desirable | Between 2.6 to 3.3 | Between 100 to 129 |
| Borderline High | Between 3.4 to 4.0 | Between 130 to 129 |
| High | Between 4.1 to 4.8 | Between 160 to 129 |
| Very High | 4.9 & above | 190 & above |
| Total/ HDL Ratio | Mmol/L |
|---|---|
| Normal | High |
| Below 4.5 | 4.5 and above |
| Triglycerides | Mmol/L | Mg/dL |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal | Below 1.7 | Below 150 |
| Desirable | Between 1.7 to 2.2 | Between 150 to 199 |
| Borderline High | Between 2.3 to 4.4 | Between 200 to 399 |
| High | 4.5 & above | 400 & above |
HDL is the good cholesterol in our body and is increased through exercise. High level of HDL reduces arthrosclerosis and the risk of heart attack.
LDL cholesterol is closely associated with increased risk of heart attack and stroke. Your doctor will assess your risk factors (diabetes, smoking, hypertension, family history) and prescribe medication for control if LDL levels are high. LDL cholesterol is reduced through dietary discretion (intake of low cholesterol food), exercise and cessation of smoking.
Triglyceride is a form of fat often associated with elevated LDL and total cholesterol levels and uncontrolled diabetes. An elevation in triglyceride levels increases one’s risk of heart disease. Fasting lipid blood profile is recommended annually for individuals above 40 years of age.
Glucose is the main carbohydrate used by the body and can be affected by dietary intake and hormones. The inability of the body to control sugar results in diabetes in the lightest which affects 9% of our adult population.
| Blood Glucose Level | Description |
|---|---|
| Below 6.0 mmol/L | Blood glucose level is normal. No evidence of diabetes noted. |
| Between 6.1 to 6.9 mmol/L | Blood glucose level may indicate presence of fasting hyperglycemia, impaired glucose tolerance or possible diabetes. Please consult your doctor for a repeat test or an oral glucose tolerance test as further evaluation. |
| 7.0 mmol/L & Above | Blood glucose level is high. Diabetes mellitus may be present, however a single measurement is not enough to make a diagnosis.Diabetes symptom includes- Lost of weight- Excessive Thirst- Increased frequency of urinePlease see your doctor for follow up. Meantime, maintain a healthy weight by reducing the intake of sweet & sugary foods. Have more complex carbohydrates such as polished, unpolished rice & whole meal bread. If you are a known diabetic, you should see your doctor for regular follow up on dietary and medical management. |
Fasting blood sugar is recommended annually for individuals above 40 years of age.
The Liver function test comprises the following:
– Total Protein– Albumin– Globulin– A/G Ratio
– Total Bilirubin– Alkaline Phosphatase
– ALT– AST– Gamma GT (GGT)
Elevations in liver enzymes (ALT, AST, GGT) are commonly noted and can be attributed to consumption of alcohol, consumption of medication, or as a result of chronic Hepatitis B infection. Persons with known Hepatitis B infection should have this test repeated every 6 to 12 months as surveillance.When derangements in liver enzymes are noted, your doctor will review your medical history and risk factors before suggesting a retest to monitor the trend and/or an ultrasound study of the liver as further work up.
Our kidneys control the salt and water components and help to filter unwanted waste substances from our body.
The Kidney function test comprises the following:
– Sodium
– Potassium
– Chloride
– Urea
– Creatinine
– Bicarbonate
The maintenance of sodium and potassium in our body is tightly regulated. Certain hormonal states and/or medication e.g. anti-hypertensives may cause derangements which will need to be worked out.
Potassium levels may also be elevated consequent to consumption of potassium rich foods, potassium supplementation, and/or handling of the blood test specimen.
Urea and creatinine may be deranged as a result of renal impairment and dehydration.
Your doctor may request for a repeat following adequate hydration.
The bone and joint panel comprises the following:
– Calcium
– Phosphate
– Rheumatoid Factor
Calcium & Phosphate are important bone minerals. Increased levels may indicate hormonal disorders resulting in increased calcium metabolism. This may affect bone strength and present risk of osteoporosis.
Rheumatoid factor is associated with the presence of rheumatoid arthritis. A result that is positive has to be correlated clinically with symptoms of joint pains.
This is a test for uric acid. High levels may cause crystallization and tissue deposits in joints.
High uric acid can be observed in gout, a condition characterised by pain, swelling, redness and warmth of the affected joints. Uric acid may be caused by excessive intake of red meats, alcohol, bean and bean products and durians. If the uric acid is found to be high, abstinence from these food groups will be helpful.
Hepatitis A is an infectious disease which can cause acute liver swelling and yellowing of skin. It is transmitted by contaminated food or water as well as consumption of contaminated shellfish such as cockles, mussels and oysters.The test determines whether you have immunity against the Hepatitis A virus and is recommended if you
- are a known Hepatitis B carrier
- are a frequent overseas traveller
- frequently consume shellfish.
| Hepatitis A HAV IgG | |
|---|---|
| Reactive | You are immune. No vaccination against Hep A is required. |
| Non Reactive | Primary course of 2 vaccinations at 0 and 6-12 months is recommended. |
The Hepatitis B screen comprises:
- Hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg)
- Hepatitis B antibody (anti-HBsAb)
| Reactive | Non Reactive | |
|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg) | You have the Hepatitis B virus, please see your doctor for regular follow-up and screening | You do not have the virus, please refer to Surface Antibody result for management |
| Hepatitis B antibody (anti-HBsAb) | Results >10 — You are immune. No vaccination required | Results <10 – Vaccination required. (for persons who have never developed immunity from primary Hepatitis vaccination) |
Hepatitis B vaccination is now part of the national childhood vaccination programme. Hepatitis B remains infectious through transmission of blood and bodily fluids such as intravenous infusion, inadequate sterilisation and sexual intercourse. It is important to be vaccinated against Hepatitis B.
Test results are valid for up to 3 months following the test.
Should you require vaccination, please make an appointment here, or visit a family doctor near you.
Hepatitis C viral infection is the most common cause for non-A, non-B cases of viral hepatitis in the community, and there is no vaccine available at this time. It is a blood-borne virus, easily transmitted when intravenous drug users share needles, through body tattoos or piercing. Transmission through sexual intercourse and from mother to baby are relatively rare, as is transmission through blood transfusion as donated blood is screened for Hepatitis C.
Although mostly asymptomatic, individuals may experience weight loss, tiredness, nausea and vomiting, fever or abdominal pain and jaundice. Persons infected with Hepatitis C are at high risk of developing chronic Hepatitis C infection (about 75%), and although usually asymptomatic, it may progress to cirrhosis in 20-30% of patients, and liver cancer. Persons who have symptoms described above, or who fall within the high risk group should take this test.
– Free Thyroxine (Free T4)
– TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
The thyroid gland controls our basal metabolic rate (rate at which body uses energy during rest to maintain vital functions such as breathing and keeping warm).
Thyroid hormones determine the body’s metabolism, an increased in levels may result in:
– loss of weight
– increased appetite
– heat intolerance
– volatile temper
Low levels may cause the opposite to occur.
We recommend this test if you suffer from any of the above symptoms. TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone) may be performed in cases where the FT4 is too low or too high. Should derangement be noted, please see your doctor for a formal assessment. Repeat test may be conducted to ascertain the trend, whilst additional tests may also be conducted to elucidate the cause of the derangement.
Cancer markers are proteins that may be produced by cells that show increased turnover. Cancer markers have variable test sensitivities and specificities and should be taken and interpreted within the context of the patients’ medical history.
| Tumour Markers | Description |
|---|---|
| Colon & Lungs (Carcinoembryonic Antigen – CEA) | CEA may be elevated in selected cases of cancers of the large intestine & lung Smokers may also have mild elevations. |
| Liver (Alpha fetoprotein – AFP) | Liver cancer marker test (AFP), together with Liver Function Test, is recommended for people with known Hepatitis B infection. |
| Pancreas (CA 19.9) | Serum CA19-9 levels may be elevated in up to:a) 80% of patients with pancreatic cancerb) 54-89% of patients with stomach cancerc) 64% of patients with colorectal cancerThis test is also used to monitor patients who have recovered from pancreatic cancer. |
| Nose (EBV) | EBV is linked to the development of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), risk of which may be increased if you:
|
| Prostate (PSA) – for males only | In Singapore, adenocarcinoma of the prostate is the 6th most common cancer among men. Screening with PSA has the potential of early detection and treatment of organ-confined disease. |
| Testicular (Beta HCG) – for males only | Elevated Beta HCG levels may indicate testicular cancer in men. |
| Marker Ovarian (CA125) – for females only | CA125 is a protein that may be elevated in cases of ovarian cancer. |
| Breast (CA15.3) – for females only | The CA15.3 test is used to monitor metastatic breast cancer and early recurrence of breast cancer. |
Full Blood Count consists of the following tests & screens for diseases such as anemia (low haemoglobin), clotting disorders, leukemia and infections.
- Haemoglobin
- RBC (RCC)
- WCC (TWDC)
- 5 Part Differential Count
- Platelet Count
- PCV – MCH/MCV
- MCHC
- Blood Film Comment
Haemoglobin is the red pigment within the blood cell and is responsible for carrying oxygen supply to the tissues. Haemoglobin may be low when there is chronic blood loss e.g. from piles, gastric ulcers, intestinal growths, or from thalassemia, a heriditary condition characterised by red blood cells of shorter lifespan. Low haemoglobin levels should be followed up with your doctor so as to elucidate the cause as they can cause lethargy and giddiness.
Elevated haemoglobin levels may be observed in chronic smokers.
WCC (TWDC) represents the white cell count of our body. This may be elevated in states of infection or blood disorders e.g. leukamia. Marginally low levels may be noted following a clinical infection. The arrangements of the white blood cell ought to be followed up by your family doctor.
Platelets play a vital role in causing bleeding to stop. Peripheral blood film studies reflect the state of the red blood cells when viewed under the microscope.
Helicobacter Pylori is known to be a possible cause of gastric ulcers. This test is used to indicate the presence of a past or current infection.
A positive Helicobacter antibody test ought to be correlated clinically if there is active symptoms of gastritis.
If there is gastric pain, triple therapy may be prescribed by your doctor to eradicate possible Helicobacter infection.
The cardiac profile test comprises of special lipoproteins, Apolipoprotein A1, Apolipoprotein B, Apolipoprotein A1/B ratio and C-reactive protein. Together with the cholesterol levels, it allows for better understanding of the cardiac risk profile.
Apolipoprotein A1 and B
Apolipoprotein A1 is the major protein component of HDL (high density lipoprotein) in blood. It helps to move fat and cholesterol from tissues to the liver for excretion. A low level of Apolipoprotein A1 indicates inadequate HDL, whilst a high level is not of concern.
Apolipoprotein B, especially when associated with elevated LDL levels, increase the risk of plague formation and artherosclerosis. A high level of Apolipoprotein B is not desirable, whilst a low level is acceptable.
| Markers | Ref range (g/L) |
|---|---|
| Apolipoprotein A1 | 0.94-1.78 |
| Apolipoprotein B | 0.62-1.33 |
| Apolipoprotein B/A1 ratio | 0.22-0.80 |
Hence a high Apolipoprotein B/A1 ratio implies inadequate HDL or excessive LDL.
C-reactive protein
A hs-CRP (high sensitivity C-reactive protein) test may be used to help identify risk of cardiovascular disease. It’s interpretation should be made in combination with other risk factors such as elevated LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, cigarette smoking, hypertension and diabetes.
Elevated levels of hs-CRP in healthy persons may suggest an increased risk of heart attack, stroke and peripheral arterial disease.
| wr-CRP | CVD Risk |
|---|---|
| <1.0 mg/L | Low risk for CVD |
| <1.0-3.0 mg/L | Average risk for CVD |
| <3.0 mg/L | Increased risk for CVD |
| >5.0 mg/L | Suggestive of infection/other sources of inflammation |
Homocysteine
Homocysteine is a type of amino acid used in the body to make proteins. Normally, vitamin B12, vitamin B6 and folic acid convert homocysteine into other substances needed in the body. High levels of homocysteine may be associated with accelerated artherosclerosis, heart disease and stroke. Reduction in intake of food rich in cholesterol, simple sugars, oil and fat, as well as in increase in physical exercise will help to correct the above factors and reduce the risk of artherosclerosis, ischemic heart disease and stroke.
Vitamin D promotes the absorption and metabolism of calcium and phosphorus. Deficiency can lead to bone weakness in adults. 25-hydroxyvitamin D test is usually ordered to identify a possible deficiency in Vitamin D.
Vitamin D is synthesised by the skin upon exposure to natural sunlight. Deficiencies in Vitamin D typically reflect an inadequate active lifestyle with consequent reduced exposure to sunlight.
– Syphilis Antibody– RPR if Syphilis Antibody is positive
– TPHA if Syphilis Antibody is positive
This test screens for sexually transmitted infection (syphilis). If untreated, it can cause chronic condition such as:
– Brain & spinal cord damage
– Blindness
– Insanity
– Miscarriage
– Birth defects in pregnant woman
– Occasionally fatal
Syphilis is an uncommon disease in this current day and age. If VDRL is positive, a secondary confirmatory test will be conducted.
An Electrocardiography (ECG) is a recording of the heart’s electrical activity over a short period of time by means of skin electrodes.
The ECG test is useful as a screening test to detect abnormal heart rhythm, previous heart attack or an enlarged weakened heart. It is a useful screening test as a baseline, especially for persons with underlying disease like hypertension, diabetes and high cholesterol.
An abnormal ECG should be followed up with a cardiologist. Further tests like an exercise treadmill test, 2D-echocardiogram, calcium scoring, or even an angiogram may be necessary.
The Bone Mineral Densitometry (BMD) is a test to measure the mineral density of a person’s bone. The measurements are generally useful to assess a person’s risk of developing osteoporosis.
Tonometry is a test used to determine the fluid pressure inside the eye (intra-ocular pressure), useful in the evaluation of patients at risk of glaucoma.
Glaucoma is an eye disease in which the increased fluid pressure causes damage to the optic nerve and blindness. In Singapore, approximately 3% of persons over 50 yrs of age have glaucoma.
This test is useful as a baseline test, and especially for those with underlying disease like diabetes, hypertension, steroid use, and family history of glaucoma. An intra-ocular pressure of >21 mmHg should be followed up with an ophthalmologist.
The Pap smear test is useful for early detection of cervical cancer, which is curable when detected early.
Cervical cancer is the 10th most common cancer amongst females in Singapore, and accounts for an estimated 70 deaths annually.
The test is recommended for women between 25-64 years old, the initial test being performed once a lady is sexually active, and subsequent PAP smear tests should be performed every 2-3 years.
An abnormal Pap smear result should be followed up with your doctor.
Chest x-rays are useful in picking up abnormal conditions involving the lungs, heart and great vessels.
It is typically performed as the first imaging test for symptoms of shortness of breath, persistent cough, chest pain, chest injury or fever. Pneumonia, heart failure, emphysema, lung cancer and other medical conditions can be diagnosed or suspected on a chest x-ray. Low doses of radiation are used to create an image of the chest.
Do not take a chest x-ray if you are or suspect that you are pregnant.
Breast cancer is the most common cancer among Singaporean women. Every year, more than 1000 women are diagnosed, and over 400 die from breast cancer.
Mammography is recommended annually for women over 40 years of age and once every 2 years for women over 50 years of age. It is useful for detecting the presence of cancerous lumps before they are felt by hand.
Low doses of radiation are used to generate an image of the breast to look for characteristic masses or microcalcifications. Abnormal mammograms should be followed up with a breast surgeon.
An ultrasound abdomen uses sonography or high frequency sound waves to produce images of the internal organs of the abdomen including the liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas and kidneys.
A pelvis ultrasound displays images of pelvic organs such as the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes. the pelvic structure.
Both are useful in aiding investigations of abnormalities in the abdomen or pelvis evidenced by abdominal or pelvic pain, and detect common diseases like fatty liver, gallstones, renal calculi.
This test is recommended as a baseline, and for persons with risk factors like obesity, high cholesterol or who have abdominal or pelvic pain.
An ultrasound prostate uses sonography or high frequency sound waves to produce images of the prostate. This test is commonly used for evaluation of the prostate gland in men with elevated prostate specific antigen (PSA), or with abnormal urinary symptoms.
PSA is present in small quantities in the serum of men with healthy prostates but is often elevated in the presence of prostate cancer, infection or hypertrophy. Abnormal results should be followed up.
Ischemic heart disease is the 3rd leading cause of death in Singapore, accounting for about 18% of deaths in Singapore.
An exercise treadmill test is performed by recording the electrocardiograph (ECG) of the heart whilst exercising on a treadmill machine. It allows assessment of the heart in response to stress and is useful for diagnosing ischemic heart disease, especially in persons with high cholesterol, hypertension and diabetes, family history of heart disease, shortness of breath or chest discomfort with exertion.
Follow up of abnormal test results with a cardiologist is recommended.
This test assesses the urine sample biochemically and under the microscope.
Detection of abnormalities eg: presence of protein, glucose, ketones, red and white blood cells, epithelial cells, crystals, casts, yeast or bacteria in the urine, or abnormal pH or specific gravity, may suggest underlying urinary tract infection, diabetes, kidney stones or kidney disease.
This test is useful as a baseline in healthy individuals, and particularly important in persons with diseases like hypertension, diabetes and kidney disease. It is advisable to consult a doctor for advice, repeat the test and follow up accordingly.
Ladies should avoid doing this test within 1 week of menstruation.
The Urine Microalbumin/Creatinine Ratio (ACR) test detects the presence of tiny particles of protein in the urine, and is useful for identifying early signs of kidney damage, especially in persons with underlying disease like hypertension, diabetes or congenital kidney disease.
An elevated ACR level should be followed up with a doctor.
| Category | ACR (mg/mmoL) |
|---|---|
| Normal | <2.5mg/mmoL (male)<3.5mg/mmoL (female) |
| Microalbinuria | 2.5 to 30 mg/mmoL (male)3.5 to 30mg/mmoL (female) |
| Macroalbuminuria | >30 mg/mmoL (male/female) |
This test is one of the screening tools for colorectal cancer where blood is not visible to the naked eye and is recommended screening test for all above 50 years old. If present, it may indicate bleeding from the gut caused by piles, growths or infections.
Positive test result should be followed up with colonoscopy.Lifetime probability of an individual developing colorectal cancer is approximately 5%. It is recommended that one abstains from taking red meat 3 days before the test.


