All About Vaccinations

Many of us fondly remember standing in line in school, waiting for our turn for health screening and immunisation conducted by the School Health Service. As adults, did you know that there are various vaccinations available to keep you protected, especially if you travel, or are at risk due to underlying disease and age?
Vaccinations are affordable
Eligible Singaporean adults can receive government subsidies of between $35-125 for recommended vaccines listed in Singapore’s National Adult Immunisation Schedule (NAIS), administered at polyclinics and CHAS GP clinics.
To illustrate, this means that for these specific vaccines administered at CHAS GP clinics, eligible Pioneer Generation card holders pay only $9-$16 per vaccination dose, whilst eligible Merdeka Generation and CHAS Blue and Orange card holders pay only $18-31 per vaccination dose. All other eligible Singaporeans pay between $35-63 per vaccination dose. (Terms and conditions apply).
In addition, up to $500 per medisave account a year (under the MediSave500 scheme) can be utilised to defray the cost of vaccinations recommended in the NAIS.
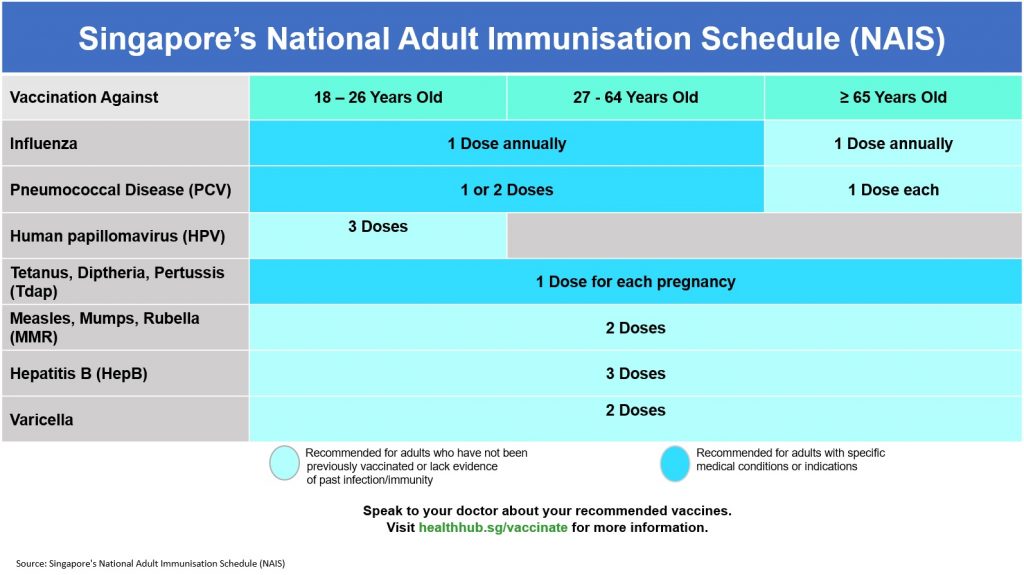
Our Minmed clinics offer the following adult vaccinations:
- Influenza vaccination
- Pneumococcal vaccinations
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccinations
- Tetanus, Diphtheria, Pertussis vaccination
- Measles, Mumps, Rubella vaccination
- Hepatitis B vaccination
- Hepatitis A vaccination
- Chickenpox /Varicella vaccination
Why vaccinate?
So what do these vaccinations do? In essence, these eight types of vaccines protect against twelve diseases through simple injections.
Influenza vaccination
Influenza, otherwise known as the “flu”, is a more serious condition compared to the common cold. Highly contagious, the flu virus spreads through droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes or talks, or through contaminated surfaces, food and drinks. The flu virus causes seasonal outbreaks and epidemics, and in Singapore the flu season typically occurs between December and February, and between May to July.
Flu symptoms include high fever, cough, sore throat, runny or blocked nose and body ache. Severe cases can lead to complications such as pneumonia, bronchitis, ear infection, sinusitis and meningitis.
Adults and children older than six years of age should receive the influenza vaccination annually.
Pneumococcal vaccination
Streptococcus pneumonia, also known as pneumococcus, causes bacterial infections such as pneumonia, meningitis, and middle ear infections which can cause severe illness. Vulnerable persons below the age of two or above the age of sixty five are particularly susceptible. Depending on the systems affected, symptoms can include fever, severe headache vomiting, runny nose, cough and breathlessness.
The two types of pneumococcal vaccination are the PCV vaccine for infants and the PPSV23 for those aged two and above where indicated.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination
Commonly known to be associated with cervical cancer, the human papillomavirus is a group of viruses that can cause vaginal and anal warts, and cancers of the vagina, penile and anal cancer.
The HPV vaccination is recommended for young females from 9-26 years old, preferably before they become sexually active. It’s importance is reflected in the vaccination being included as part of the National Childhood Immunisation Schedule and the National Adult Immunisation Schedule (NAIS) for the target population of females aged 9 to 26 years old.
Apart from vaccination, women should also undergo screening for cervical cancer via the PAP smear or HPV test.
Tetanus, Diphtheria, Pertussis vaccination
This 3-in-1 vaccine protects against tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (whooping cough). Given in childhood according to the National Childhood Immunisation Programme, the immunity levels can decline over time.
Adults may receive a booster vaccination every 10 years.
Measles, Mumps, Rubella vaccination
Measles is a highly contagious disease causing symptoms like runny nose, cough, fever and generalised rash. Whilst most recover, some can develop complications like pneumonia and brain and liver inflammation.
Also highly contagious, mumps causes painful swelling of the salivary glands, fever, headache and sore throat. The most serious complications include testicular infection and possible male infertility, hearing loss, and infection of the central nervous system (meningoencephalitis).
Rubella, commonly known as “German measles”, is a highly infectious but mild infection that commonly affects children. It can cause serious birth defects in the unborn child when a pregnant woman is infected.
The MMR vaccine protects against these three viruses, and is usually administered to children at age 15 and 18 months. Women who intend to conceive should be screened for rubella antibodies and be immunised at least three months before conception.
Hepatitis B vaccination
Hepatitis B is a viral infection of the liver, spread through contaminated blood and blood products, bodily fluids during sexual contact, from an infected mother to the child during childbirth, and using contaminated needles, for example with acupuncture or tattooing.
Some symptoms include jaundice, fever, tea coloured urine, pale stools, tiredness and nausea. Serious complications such as chronic hepatitis B infection, cirrhosis, liver failure and liver cancer can occur.
Children in Singapore receive the Hepatitis B vaccination as part of the National Childhood Immunisation Schedule (NCIS) A simple blood test to screen for Hepatitis antibodies is useful to ascertain if vaccination is needed.
For adequate immunity, a complete course of three Hepatitis B vaccines is necessary.
Hepatitis A
Presenting with symptoms similar to Hepatitis B, the Hepatitis A virus causes liver infection which can range from mild to severe illness. Prolonged fatigue experienced by infected persons sometimes requires months for adequate recovery for return to work and daily life.
Commonly spread by food or water contaminated with the faeces of an infected person, it is therefore prevalent in areas with poor sanitation, personal and food hygiene.
A blood test to screen for Hepatitis A antibodies is useful to alert one of the need for vaccination, which requires two doses for complete immunity.
Twinrix vaccination
The twinrix vaccination is a combination of Hepatitis A and B vaccines in one syringe. A complete course requires three doses confers immunity.
Chickenpox (varicella) vaccination
Chickenpox, commonly contracted in childhood, plagues the infected person with fever, small tiny vesicular itchy rashes on the body. Caused by the varicella-zoster virus, this highly contagious disease can be spread through droplet infection or contact with articles soiled with the fluid from blisters of an infected person. Complications include pneumonia, encephalitis and in pregnant women, birth defects or stillbirths. Chickenpox can be prevented through vaccination.
Dr Lisa Chen
M.B.B.S. (Singapore) Grad. | Dip. Occupational Medicine
Dr Lisa Chen is a deeply passionate family physician and designated workplace doctor with an endearing commitment to the successful attainment of health and wellness at individual, workplace and community levels. Having worked widely with family practice clinics and major medical disciplines, she is thoroughly committed to the promotion and sustenance of health and quality of life for everyone.
Dr Lisa Chen
M.B.B.S. (Singapore) Grad. | Dip. Occupational Medicine
Dr Lisa Chen is a deeply passionate family physician and designated workplace doctor with an endearing commitment to the successful attainment of health and wellness at individual, workplace and community levels. Having worked widely with family practice clinics and major medical disciplines, she is thoroughly committed to the promotion and sustenance of health and quality of life for everyone.
